Cervical osteochondrosis can cause more intense clinical symptoms than such degenerative changes in other parts of the spine. This is because the disruption of blood circulation in this area can lead to a lack of oxygen in the brain. Symptoms may vary depending on the extent of the pathological process.
For at-home treatment, with the permission of a specialist, you can use medications designed to stop inflammation and pain. Therapeutic exercises and massage are effective, but they also have their limitations. In addition to these conservative measures, folk remedies can be used.
reason
Osteochondrosis in the cervical region can occur due to a variety of factors. The reasons are the same for men and women:
- incorrect posture;
- Scoliosis;
- overweight;
- passive lifestyle;
- Spinal cord injury;
- excessive physical activity;
- metabolic diseases;
- genetic predisposition;
- Nervous shock, frequent stress;
- The back muscles in the neck area are constantly tense.
The mechanism by which osteochondrosis occurs is related to an increase in the load on this part of the spine to compensate for spasticity of the neck muscles. As a result, blood circulation in this area is disturbed and degenerative dystrophic changes occur in the neck area.
symptom
The symptoms of the disease depend on the stage of the pathological process. Cervical osteochondrosis has a total of 4 stages of development:
| stage | characteristic symptoms |
|---|---|
| first | Slightly. There is usually a syndrome of mild muscle ligament tension and mild pain in the area of the nerve bundles. |
| second | The intervertebral disc is herniated, and as a result the intervertebral space decreases and the annulus fibrosus begins to gradually collapse. Pain syndrome may be exacerbated due to compression of nerve endings |
| third | Symptoms get worse: The pain becomes permanent and begins to radiate to the shoulders and upper extremities. When the affected area is palpated, discomfort increases dramatically, and as the hernia develops, there may be numbness and tingling in the fingers. Limited neck movement, joint stiffness |
| fourth | It is characterized by the complete destruction of the intervertebral disc, resulting in compression of the connective tissue. As a result of these changes, a person can experience the following symptoms:
|
The symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are different from diseases that affect other parts of the spine. This is due to the location of this sector of the vertebrae closer to each other. The relatively small height of the intervertebral disc results in a dramatic onset of clinical symptoms even with mild pathological changes in its structure. Osteochondrosis of the neck region often occurs with compression of the nerve roots and spinal cord.
Symptoms in this condition can vary, depending on which vertebrae experience degenerative dystrophic changes. Usually the main symptom is neck pain, which can spread to all parts of the body: breastbone, arms, jaw, etc. A characteristic crunch may occur when the head is turned. Compressed nerves and blood vessels can cause numbness in the tongue and fingertips. Pain syndromes may vary:
| syndrome | describe |
|---|---|
| root | due to nerve compression. The pain is decreasing and sharp. It extends to the shoulders, forearms and fingertips. With radiculopathy, goosebumps and tingling may be experienced. Another characteristic is decreased elasticity, skin firmness, slight swelling and the appearance of whitening. |
| vertebral artery | Occurs when a vertebral artery is squeezed. Pain has a throbbing or burning character and affects the glabellar area, temples, nape, and top of the head. Usually it is constant, but it can be episodic. Discomfort increases after prolonged exercise or in uncomfortable positions. When debilitated, symptoms may expand, manifesting as nausea and loss of consciousness. If blood flow to the brain is blocked, symptoms such as:
|
| Migraine | It is caused by stimulation of the sympathetic ganglia, which can lead to disease in the brain. These include pathologies of vascular reactivity and blood circulation. This can cause the following symptoms:
|
| hypertension | It is characterized by elevated intracranial pressure. In hypertensive syndromes, the headache is sudden and may be accompanied by nausea and vomiting. Exacerbations lead to increased body temperature |
treat
It is not possible to completely cure osteochondrosis and permanently eliminate its manifestations, but it is possible to eliminate symptoms. For osteochondrosis in the neck area, you can use conservative approaches aimed at reducing pain syndromes, spinal root dysfunction, and preventing complications of the disc degenerative process.
For this purpose:
- drug;
- massage;
- exercise therapy (physiotherapy exercise);
- Folk remedies.
Self-treatment with spondylosis is impossible. All treatments and methods used should be discussed with a specialist and applied at home with his approval. In cases where conservative methods have not worked (if you cannot get rid of the pain), you should consult your doctor as surgery may be required.
drug
For cervical osteochondrosis, analgesics are used to relieve pain. They can be taken in tablet and capsule form. However, long-term use of analgesics will stimulate the mucous membranes of the digestive tract, so it is not advisable to take them frequently.
To relieve inflammation, steroids, hormone drugs are used. These drugs can relieve pain if they do not affect the pathological process itself. Typically, topical medications are used in the form of ointments or tablets based on hydrocortisone, dexamethasone, and prednisolone.
To restore the intervertebral disc, chondroprotective agents are recommended. They contain substances that can replace the components of cartilage tissue - hyaluronic acid and chondroitin. However, the effectiveness of these drug groups is only possible with long-term use.
Muscle relaxants are used to relax muscle structures. They help further reduce pain. They are used in the form of injections. For the treatment of osteochondrosis, drugs containing glycerol and benzimidazole are most effective.
Vitamins are necessary to improve the conductance of nerve fibers and the state of the peripheral nervous system. Use water-soluble vitamins B1, B6, B12 and fat-soluble vitamins A, C, D.
The most convenient forms of medication to treat osteochondrosis at home are ointments and gels. There are various types of topical agents: warm, anti-inflammatory, pain relievers.
massage
For cervical osteochondrosis, massage should be done with care and without excessive force. Improper manual therapy can lead to complications. Pay attention to the neck, upper back and collar area when massaging.
It is recommended to perform the procedure in the supine position. If the patient is unable to take it, sit for treatment. Assistants can use the following tips and tricks:
- Stroking - superficial effects on the skin. Do this with your hands or fingertips from your head to the upper third of the middle of your back. From the bottom of the neck, you can resort to zigzag strokes.
- Push-ups - Impress your fingers (thumb and forefinger) deep into the skin through the neck. This technique is used on tissue away from the vertebrae.
- Friction - Development of the collar area to warm the skin and increase blood flow. Use with extreme care not to affect the spinous processes of the vertebrae. Friction can be replaced with a motion like sawing or circular swiping.
- Kneading - effects on deep tissue. They are mostly used in areas away from the neck area - upper back with limited use.
The patient can perform massage and most - seated positions. To do this, he can use techniques such as stroking and circling the neck and shoulders. It is recommended to combine self-massage with rubbing ointments designed to increase blood flow and relieve pain.
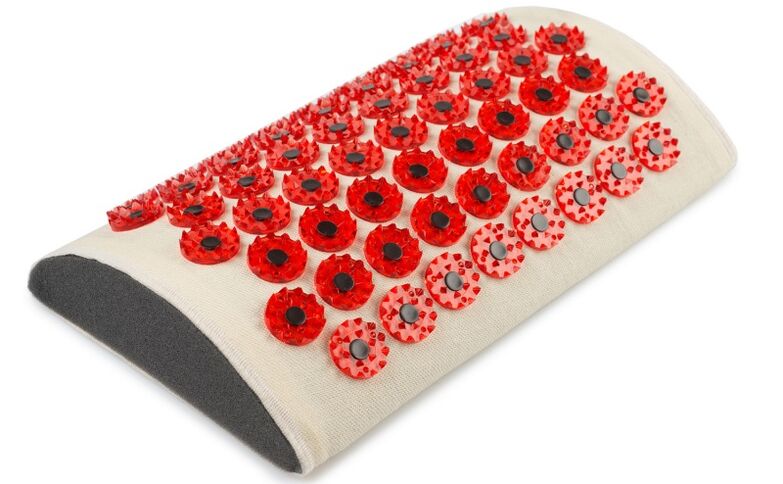

Manual therapy can be performed passively using the Kuznetsov applicator, a special device with plastic spikes that acts on acupuncture points in the neck area. Acupressure is useful because it stimulates skin receptors that are responsible for the body's physiological processes. In some cases, the applicator can help permanently and effectively reduce pain, normalize blood circulation, and restore patient performance.
However, the use of medical devices has certain contraindications. Not for use in infectious, skin, tumor and vascular diseases. Despite the simplicity of the device, it is recommended that you first consult your doctor about the possibility of using it. If there are unpleasant feelings during treatment with the applicator, the health condition deteriorates, then it should be abandoned.
For effective prevention, you can sleep with a special orthopedic pillow. It was found that resting the head in an uncomfortable position for 8 hours would contribute to the development of the disease due to the disease of the discs in the neck.
The advantage of an orthopaedic product is that it is not only a preventive tool, but also a therapeutic tool - this is known as postural therapy. With the right choice of sleep pillow, neck pain will be significantly reduced and there will be no need for dangerous self-massages with vigorous exercise.
exercise therapy
Therapeutic exercise is one of the most effective methods of conservative treatment. However, certain rules must be followed. It is best to have a set of exercises established by an expert and conduct the first class under his supervision.
Suggestions for therapeutic exercises:
- Clothing should not restrict movement;
- The exercise should be performed in a well-ventilated area;
- It is recommended to take classes no earlier than half an hour after meals;
- In a week, it is necessary to repeat the exercise up to 4 times;
- All movements should be performed smoothly, as fast movements can cause complications;
- It is necessary to control the pulse;
- If pain occurs during exercise, you need to replace them with stretching and relaxing movements;
- The intensity of the grade and load must be gradually increased;
- It is advisable to alternate physical therapy exercises with gymnastics to ensure proper breathing.
Exercise therapy for cervical osteochondrosis is not performed in the following cases:
- During periods of exacerbation of the disease, pain is evident both during exercise and at rest.
- Dizziness is caused by impaired blood circulation due to vertebral instability.
- Some acute illnesses show signs of inflammation.
- Diagnosed with cancer at any stage.
- Impaired blood coagulation, i. e. a risk of thrombosis or a tendency to bleed.
- poisoning.
- Cardiovascular disease and arterial hypertension are present in the decompensated phase.
- Diagnosed as high myopia with fundus lesions.
For cervical osteochondrosis, the following exercises are recommended:
| starting point | set of exercises |
|---|---|
| stand at my feet |
|
| sit on the chair |
|
Appropriate and regular exercise for cervical osteochondrosis can relieve tension, increase blood flow, strengthen neck muscles, and improve vertebral mobility.
Activities such as running, jumping, swinging and pushing, and weight lifting are prohibited. You should also avoid exercises that focus on hands and suspension. With the permission of the doctor, if the patient has previously trained, the exercise may be performed, but must have a complete exercise program.
Ethnoscience
It is recommended to use the following external Chinese medicines for the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis:
- Horseradish leaf compress. The plant has anti-inflammatory properties. Horseradish leaves should be young and fresh. Dip them in boiling water for a few seconds, then apply them to the cervical spine immediately. From above, the app is covered with cellophane and a warm scarf. Compression remains as long as possible. It is recommended to do a bandage in the evening and wash it in the morning.
- Alcohol compress. You will need 300ml of medical alcohol, 10 dimethicone tablets (powder), 10ml of iodine and 10ml of camphor alcohol. All ingredients are well mixed together. In the resulting solution, gauze is moistened, applied to the sore neck, covered with polyethylene and covered with a warm scarf. Do not leave the compress for more than 2-3 hours as alcohol can irritate the skin. Even with minor injuries, this method is contraindicated.
- A compress of potatoes and honey. 1 large raw potato, grated and diluted with 2 tablespoons. l. Honey. The resulting mixture was applied to the fabric, which adhered to the painful area. Remove the compress after 2 hours.
- Salve with hops. 1st. l. Powder obtained from hop cones, ground with 1 tablespoon. l. Fresh butter. Apply the resulting ointment to the painful area and insulate.
- Indoor decoction. For the roots of the second year plant, use 2 tablespoons. l. Pour in a glass of boiling water. The solution is boiled at low temperature for 10 minutes and then filtered. Inulin therapy is used for compression applied to the spine. Delete the application after 20 minutes. This remedy is also used in the bath, while the amount of raw material is increased to 10 tablespoons. l.
For pain relief, the following recipes are recommended by mouth:
- Tincture on pine sprouts. They are harvested in the spring, selecting specimens that are at least 15 mm and no more than 20 mm in size. The collected ingredients are thoroughly washed, ground in a coffee grinder, and diluted 2: 1 with sugar. Mix these ingredients together, remove and store in the refrigerator for 2 weeks. The resulting remedy is taken in 1 teaspoon. 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 3 weeks. The tincture can be kept in the refrigerator for up to 1 year.
- Celery juice. Grate the roots of the plant with a grater and squeeze out the juice. They drink 1 tablespoon. l. 3 times a day, before meals. Sometimes 1 tablespoon is mixed. l. Take the juice with a glass of boiling water for 2 hours. This composition is taken in 1 tablespoon. l. 4 times a day one hour before meals.
- Celery root infusion. 3 grams of raw materials are filled with 500 ml of boiled water. After it is completely cooled, drink 20 ml before meals.
- Bay leaf decoction. Put 12 grams of ingredients in an enamel dish, pour in 300 ml of cold water, boil for 5 minutes, then soak for 3 hours and filter. The tool is consumed in small bites throughout the day between meals. The rest are drunk before bed. The course of treatment is 4 days, followed by a week off and repeating. As a preventive measure, treatment is given every spring.
For cervical osteochondrosis, you can use herbal teas with general strengthening properties. Useful drinks and uses:
- bilberry and birch leaves;
- chamomile;
- Bodhi flower;
- wild rose;
- Calendula;
- Hypericum;
- ponytail;
- Motherwort.